Summary of questions. The answers are further below.
Α. Why do we say extra virgin olive oil? What is the difference between virgin olive oil and ordinary olive oil?
B. What are the quality criteria for extra virgin olive oil?
C. Black or green olives? What is their difference?
D. health claim for the extra virgin olive oil
A. Why is it called extra virgin olive oil? What is the difference between virgin olive oil and ordinary olive oil?
There are 3 main categories of olive oil on the supermarket shelves:
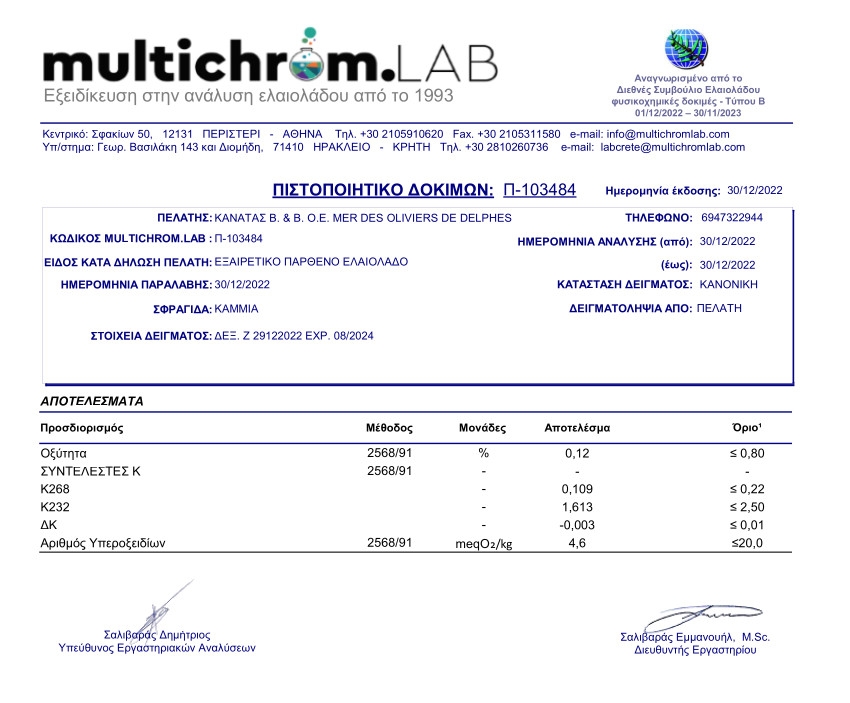
- extra virgin olive oil is produced only by natural and mechanical processes, with perfect aroma and taste, with free oleic acidity not exceeding 0.8% and with other characteristics in accordance with those provided by the European Community Regulation 2568/91.
- Virgin olive oil is produced only by physical and mechanical processes, with good organoleptic characteristics, with a free oleic acidity not exceeding 2.0% and with other characteristics in accordance with those provided for by regulation 2568 / 91 of the European Community.
- Olive oil: “is the mixture of refined olive oil (by chemical methods) and edible virgin olive oil whose free oleic acidity does not exceed 1%. Refined olive oil is obtained by refining, that is to say by chemical methods (neutralization, deodorization, discoloration) of the disadvantaged virgin olive oil ”.
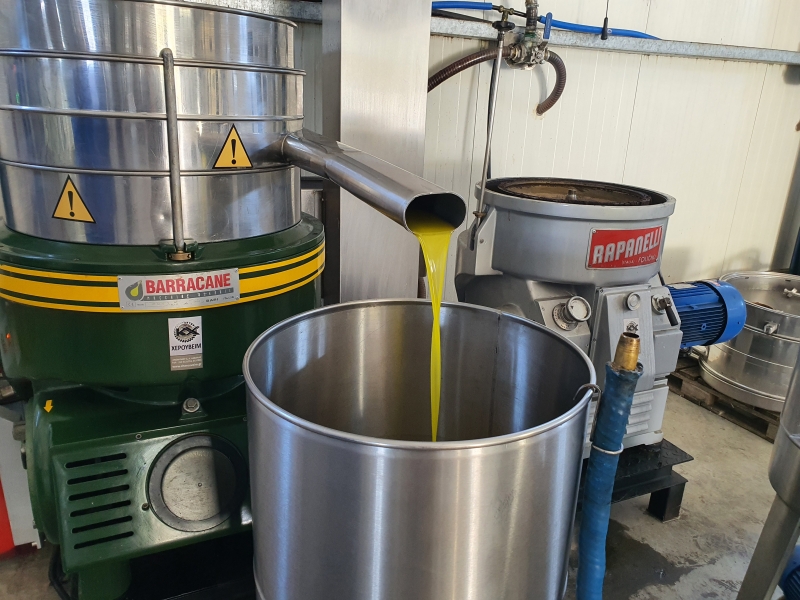





B. What are the quality criteria for extra virgin olive oil?
The criteria for evaluating olive oil are mainly 4, as follows:
The free oleic acidity
In extra virgin olive oil, the free acidity must not exceed 0.8%
Number of peroxides
The number of peroxides is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an oil at the primary stage, based on the detection of peroxides as indicators of tangency.
UV absorption
It is measured by two constants named K232 and K270 (or K268).
The K232 shows the intermediate percentage of oxidation of the components of olive oil, when this is verified in the chromatograph with a wavelength of 232 nm. If the price of the K232 is high, it is due to a scary, very slow or not modern production process.
The K270 (or K268) indicates the percentage reduction in resistance to oxidation when olive oil is checked on the chromatograph with a wavelength of 270 nm. The price of this constant depends on the freshness of the olive oil. Old olive oils or blends with old olive oils have increased the prices of K270.
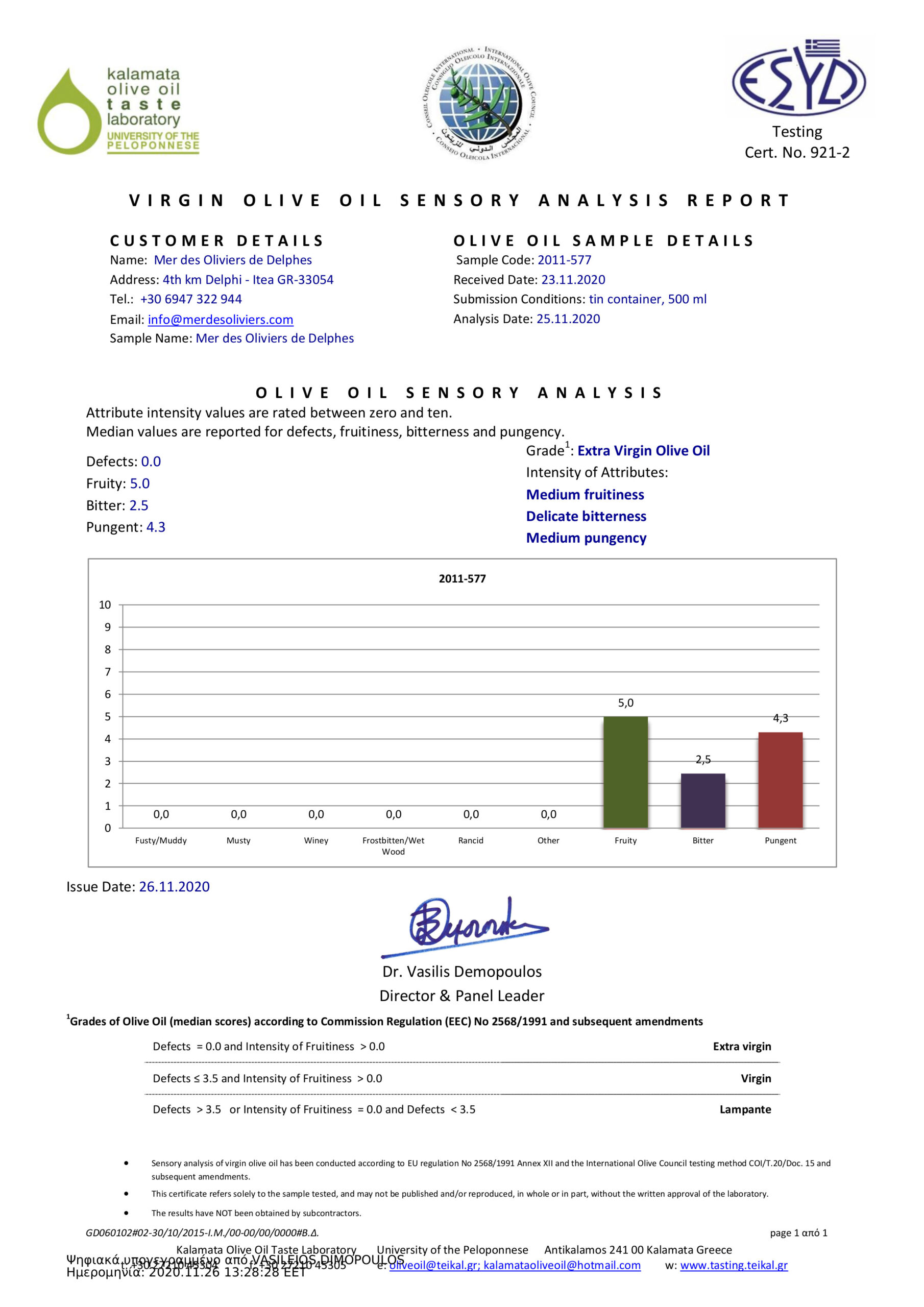
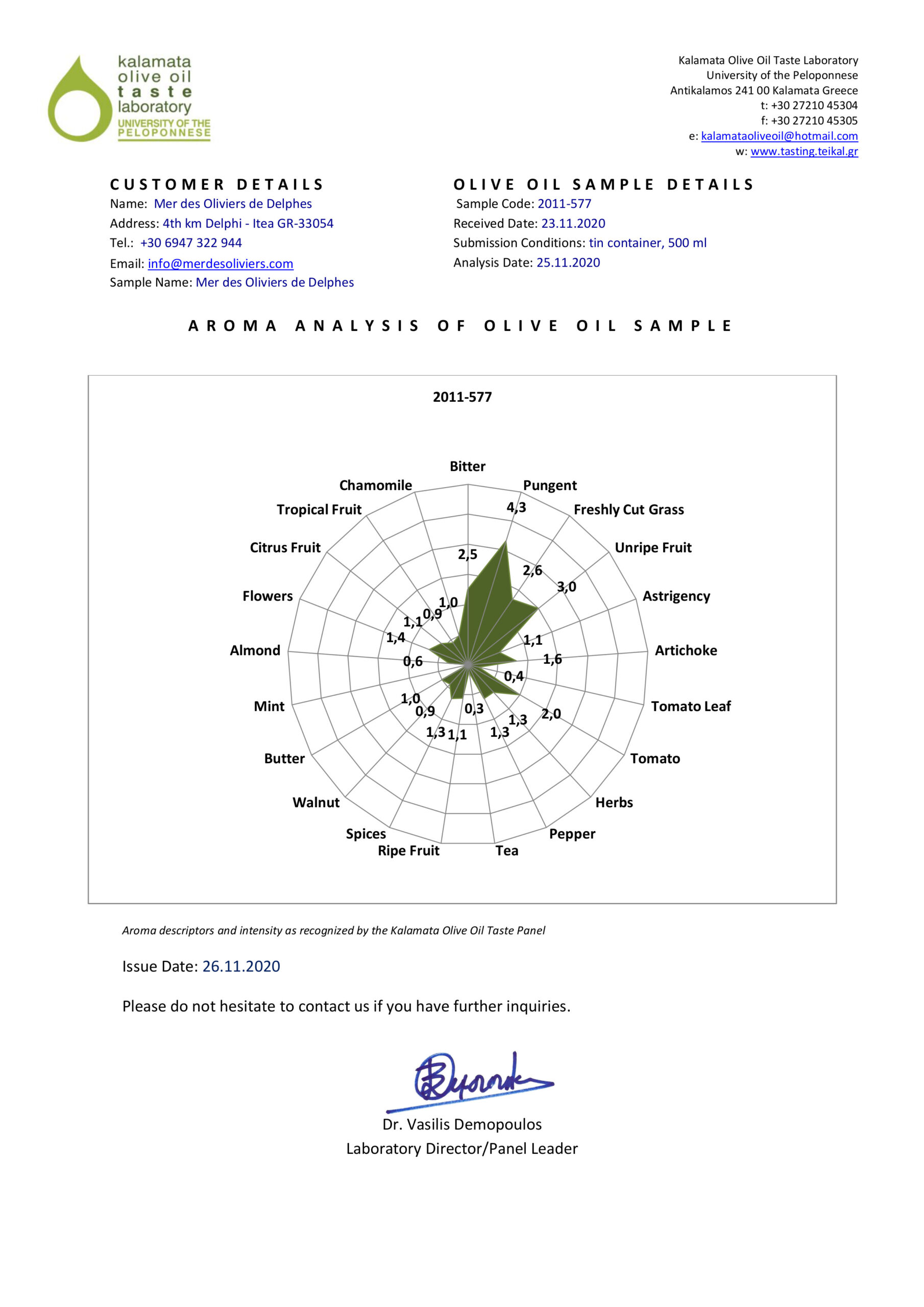
Organoleptic evaluation of olive oil
To understand how necessary the “organoleptic” (tasting) evaluation of an olive oil is, we must of course first define what it means exactly and what its value and usefulness is. In simple terms, ‘organoleptic’ (tasting) evaluation means examining an olive oil, after first smelling it (odor) and then tasting it by putting a small amount in our mouth (taste) in order to identify its special characteristics.
To correctly determine these characteristics, one must first smell a small amount of olive oil in a small glass and then try it by slowly swallowing another small amount (for example a teaspoon). This process will allow us first to see if the olive oil has a defect (“negative characteristic”) and then describe which “positive characteristics” and to what extent have we identified. The (good) positive characteristics of olive oil, according to the definition given and used worldwide by the International Olive Council, are three in number: “fruity”, “bitter” and “spicy”. A good olive oil should have these three characteristics, which are evaluated and rated by trained judges (olive oil tasters). The higher the score attributed to them, and in particular to the first, called “fruity”, the better the characterization of an olive oil.
But what is an “organoleptic defect”? It is a bad smell or bad taste that can be present in olive oil and can come from eg. pickling, moldy olives in the bags, when they have gone to the mill and waited stacked for 5 or 10 days, or usually have an unpleasant bad taste which may be due to fifteen other reasons related to the production, the preservation process etc. Warning: If an olive oil has an organoleptic defect, it cannot be called “extra virgin”! It will be classified as “virgin” if the defect is not serious or, if it is serious, it will have to be sent for serious industrial treatment to the refinery in order to get rid of all the bad characteristics and to be sold with the indication on the label “olive oil” (and not extra virgin!).
Text by Vassilis Fratzolas, Greek expert in olive oil.


C. Black or green olives? What is their difference?
First of all, it must be said that black olives are just a more mature stage than green olives. The olives on the tree first turn green, then gradually turn purple, and at the end they ripen completely, acquiring a deep black color.
Their nutritional value is more or less the same. A 15 gram serving of black olives contains 25 calories, while the corresponding amount of green 20 calories. Both contain 2 grams of fat (0.5 grams of saturated or polyunsaturated fat and 1.5 grams of monounsaturated fat). They contain less than 0.5 grams of protein, 1 gram of carbohydrates and 0.5 grams of fiber. Finally, they contain small amounts of vitamins and minerals and more precisely 2% of our body’s daily requirements for vitamin E and 1% for vitamin A.
The only difference is the amount of sodium they contain. Five black olives contain about 115-125 milligrams of sodium, or 8% of this recommended daily allowance. The same serving of green olives contains 218 to 360 milligrams of sodium, or 14 to 24% of the same guideline. So we conclude that black people are -in a sense- better, because a high amount of sodium is not good for our body.



D. health claim for the extra virgin olive oil (for olive oil containing at least 250mg of polyphenols)
“The polyphenols in olive oil help protect blood lipids against oxidative stress as part of a varied and balanced diet”
European Regulation 432/2012 (L 136 / 25.5.2012 p. 26. This health claim can only be used for olive oil containing at least 250 mg of polyphenols per 1 kg of olive oil and recommended dose is at least 20 grams of olive oil per day.

